What is Acute Cholecystitis?
Acute Cholecystitis is the sudden inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by gallstones blocking the bile duct. This leads to severe abdominal pain, nausea, and fever. If untreated, it can result in serious complications like infection, gallbladder rupture, or tissue death.
It is a medical emergency that often requires hospital treatment and, in many cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
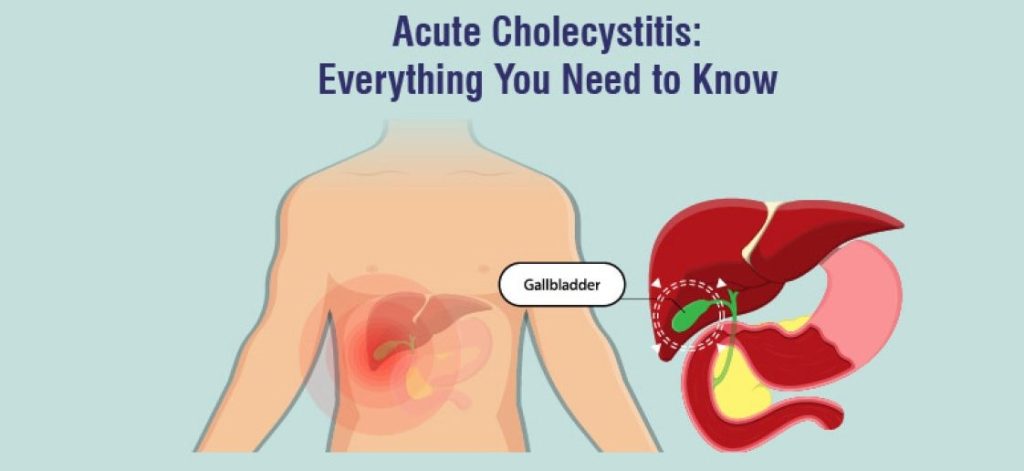
What Causes Acute Cholecystitis?
The primary cause is gallstones (hardened deposits of cholesterol or bilirubin) that block the cystic duct, preventing bile from flowing out of the gallbladder.
Other Causes & Risk Factors:
- Gallstones (90-95% of cases)
- Bile duct blockage due to tumors or strictures
- Severe illness or infections (Acalculous Cholecystitis)
- Trauma, burns, or major surgery
- Prolonged fasting or rapid weight loss
- Obesity, diabetes, or high cholesterol levels
What Are the Symptoms of Acute Cholecystitis?
Symptoms develop suddenly and can become severe within hours.
Common Signs & Symptoms:
- Severe, sharp pain in the upper right abdomen (may spread to the right shoulder or back)
- Pain that worsens after eating fatty foods
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (indicating infection)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) (if bile flow is blocked)
- Bloating and loss of appetite
How is Acute Cholecystitis Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose acute cholecystitis based on symptoms, physical examination, and imaging tests.
Key Diagnostic Tests:
- Ultrasound – First-line test to detect gallstones and gallbladder inflammation.
- CT Scan or MRI – Provides a detailed view of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- HIDA Scan (Cholescintigraphy) – Checks gallbladder function and bile duct blockage.
- Blood Tests – Detects infection, liver enzyme changes, or inflammation.
What Are the Treatment Options for Acute Cholecystitis?
Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and remove the underlying cause.
1. Hospital Treatment & Supportive Care:
- Fasting (NPO) to rest the gallbladder
- Intravenous (IV) fluids to prevent dehydration
- Pain management (NSAIDs or opioids)
- Antibiotics if infection is suspected
2. Surgery: Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy)
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Minimally invasive, preferred method)
- Open Cholecystectomy (For severe cases or complications)
3. Non-Surgical Options (If Surgery Is Not Possible):
- Gallstone removal via Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Percutaneous cholecystostomy (drain placement)
Can Acute Cholecystitis Cause Complications?
If untreated, it can lead to:
- Gallbladder infection (Empyema)
- Gallbladder rupture (Perforation)
- Tissue death (Gangrenous Cholecystitis)
- Peritonitis (Severe abdominal infection)
- Sepsis (Life-threatening infection spread)
How Can Acute Cholecystitis Be Prevented?
- Maintain a healthy weight and diet (low-fat, high-fiber foods)
- Avoid rapid weight loss or crash diets
- Stay active and hydrated
- Manage cholesterol and diabetes


